Galen Extras is a library for extending the Galen Specs Language with most common complex expressions, which allows you to have minimal code and maximum test coverage.
Here is a small example which describes all layouts of menu items on responsive website:
@lib galen-extras
@objects
menu #menu .middle-wrapper
item-* ul li
@groups
(menu_item, menu_items) menu.item-*
= Menu items should adapt layout =
@on *
| amount of visible &menu_items should be 4
| every &menu_item has height ~ 64px
| first &menu_item is inside menu 0px top left
@on desktop, tablet
| &menu_items are aligned horizontally next to each other with 0 to 5px margin
@on mobile
| &menu_items are rendered in 2 column table layout, with 0 to 4px vertical and 1px horizontal margin
Using galen-extras
Galen Extras is an embedded lib which you can add using @lib keyword:
@lib galen-extras
# Here goes the rest of your gspec file
@objects
# ...
Documentation
In this section you will find syntax explanation for all rules and examples.
Squared elements
Allows to check that element has equal width and height.
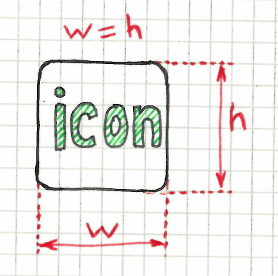
For multiple elements
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} should be squared
= Main section =
| header_icon, menu_button should be squared
For single elements
Scope: Object
Syntax: squared
header_icon:
| squared
Almost squared elements
Same as squared rule but it allows an error rate of 10%
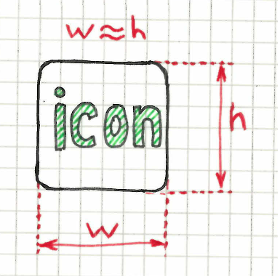
For multiple elements
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} should be almost squared
| header_icon, menu_button should be almost squared
For single elements
Scope: Object
Syntax: almost squared
header_icon:
| almost squared
Width/Height Ratio
You can check the exact ratio of width/height in percentage
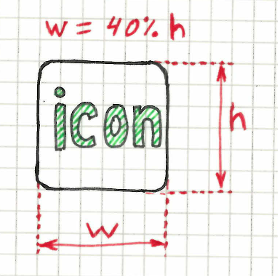
Multiple elements
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{itemPattern} should have %{ratio}% width/height ratio
| login_button, cancel_button should have 140 % width/height ratio
Single elements
Scope: Object
Syntax: %{ratio}% width/height ratio
login_button:
| 140 % width/height ratio
Testing amount of objects
In Galen you can check the amount of objects using just the 2 lines of code:
global:
count any menu.item-* is 3
But it is not very human readable. By using the rule below you can express this validation in simple sentence
Scope: Section
Syntax: amount of %{visibilityType} %{objectPattern} should be %{amount}
where visibilityType can take any, visible or absent values
e.g. amount of any elements:
| amount of any menu.item-* should be 5
e.g. testing only visible elements
| amount of visible menu.item-* should be 5
Giving a range of expected values
| amount of visible menu.item-* should be 4 to 7
or
| amount of visible menu.item-* should be > 4
Alignment of multiple elements with zero margin
A very common situation when you have elements on the page aligned either vertically or horizontally.
Horizontal
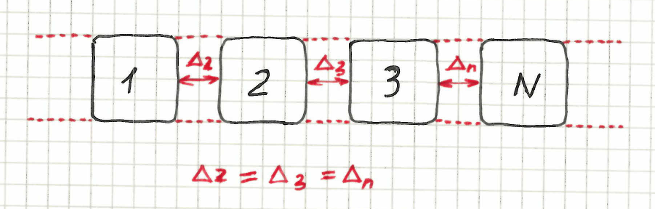
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} are aligned horizontally next to each other
| menu.item-* are aligned horizontally next to each other
Vertical
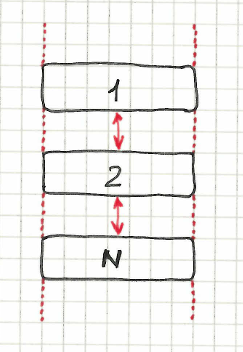
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} are aligned vertically above each other
| menu.item-* are aligned vertically above each other
Alignment of multiple elements with equal distance
A very common situation when you have elements on the page aligned either vertically or horizontally. At the same time their margin might change depending on page width.
The following rules will help you when you can’t know the exact margin and you just want to check that it is consistent.
Horizontal
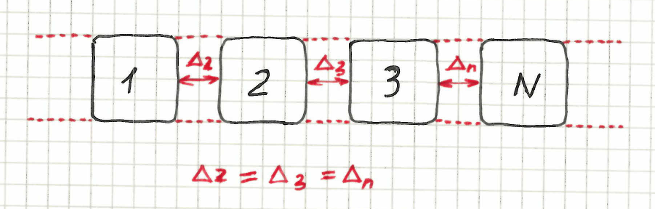
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} are aligned horizontally next to each other with equal distance
| menu.item-* are aligned horizontally next to each other with equal distance
Vertical

Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} are aligned vertically above each other with equal distance
| menu.item-* are aligned vertically above each other with equal distance
Alignment of multiple elements with specific margin
Similar to the above statement but in this case you can declare a specific margin between elements
Horizontal
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} are aligned horizontally next to each other with %{margin} margin
| menu.item-* are aligned horizontally next to each other with 5px margin
| box-* are aligned horizontally next to each other with 25 to 30px margin
Vertical
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPattern} are aligned vertically above each other with %{margin} margin
| menu.item-* are aligned vertically above each other with 5px margin
| box-* are aligned vertically above each other with 25 to 30px margin
Table layout
Allows to check that a set of elements is displayed in simple table. You can define the amount of columns for this table layout.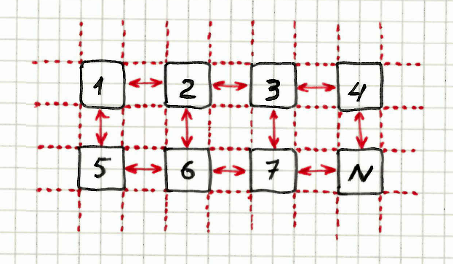
Table layout with zero margin between cols and rows
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{itemPattern} are rendered in %{columns} column table layout
| menu.item-* are rendered in 2 column table layout
Table layout with equal cols and rows margin
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{itemPattern} are rendered in %{columns} column table layout, with %{margin} margin
| menu.item-* are rendered in 2 column table layout, with 0 to 5px margin
Table layout with different cols and rows margin
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{itemPattern} are rendered in %{columns} column table layout, with %{verticalMargin} vertical and %{horizontalMargin} horizontal margins
| menu.item-* are rendered in 2 column table layout, with 0px vertical and 5px horizontal margins
Location of sides of multiple elements inside a container
The following statement checks that a set of elements is located inside specified container and that the first and last element have a specific margin from sides between the container sides.
Horizontal zero margin
Syntax: %{objectPattern} sides are horizontally inside %{containerObject}
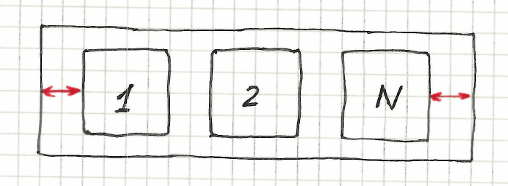
| menu.item-* sides are horizontally inside menu
Vertical zero margin
Syntax: %{objectPattern} sides are vertically inside %{containerObject}
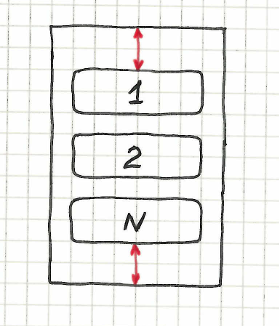
| menu.item-* sides are vertically inside menu
Custom margin for both sides
Syntax: %{objectPattern} sides are inside %{containerObject} with %{margin} margin from %{sideAName} and %{sideBName}
where sideAName and sideBName can take the following values: left, right, top, bottom
#h4. Left and Right

| menu.item-* sides are inside menu with > 0px margin from left and right
#h4. Top and Bottom

| box-* sides are inside box_container with > 0px margin from top and bottom
Common Conditions
The following common conditions allow you to insert your own code block and invoke only if condition succeeds.
If all elements are visible
Scope: Any
Syntax: if all %{objectPattern} are visible
| if all menu.item-* are visible
menu.item-*:
height 30px
If any of elements is visible:
Scope: Any
Syntax: if any of %{objectPattern} is visible
| if any of menu.item-* is visible
menu:
height 50px
If none of elements are visible:
Scope: Any
Syntax: if none of %{objectPattern} are visible
| if none of menu.item-* are visible
main:
below header 0px
Appearance of elements per breakpoints
Quite often you have elements of the website that are hidden on small devices and are only shown on large layouts.
You can use the following statements to express that behaviour
Scope: Section
Syntax: %{objectPatterns} should be visible on %{tagsVisible} but absent on %{tagsAbsent}
| twitter_button should be visible on desktop, laptop but absent on tablet, mobile
Component validations for multiple elements
Allows to specify a component check for a set of elements
Scope: Section
Syntax: test all %{objectPattern} with %{componentPath}
| test all box-* with components/box.gspec
Applying generic checks for multiple elements in a single line
This is usefull when you have repetitive specs for different elements and you don’t want to use forEach loops. Basically if you have forEach loop for one iterated object and one spec for it, you can do in a single statement using this rule.
Scope: Section
Syntax 1: every %{objectPattern} is %{spec}
Syntax 2: every %{objectPattern} has %{spec}
| every menu.item-* is inside menu 0px top bottom
| every menu.item-* has width 100px
Applying two specs for multiple elements in a single line
Similar to the above statement, this one allows to have two specs separated by word and
Scope: Section
Syntax 1: every %{objectPattern} is %{spec1} and has %{spec2}
Syntax 2: every %{objectPattern} has %{spec1} and is %{spec2}
Syntax 3: every %{objectPattern} has %{spec1} and has %{spec2}
Syntax 4: every %{objectPattern} is %{spec1} and is %{spec2}
| every menu.item-* is inside menu 0px top bottom and has width 100px
Checking only first element from given expression
Often when working with set of elements you need to check only the first one or the last
Syntax 1: first %{objectPattern} is %{spec}
Syntax 2: first %{objectPattern} has %{spec}
| first menu.item-* is inside menu 0px top bottom
| first menu.item-* has width 100px
Checking only last element from given expression
Same as above, but this time it checks the last element
Syntax 1: last %{objectPattern} is %{spec}
Syntax 2: last %{objectPattern} has %{spec}
| last menu.item-* is inside menu 0px top bottom
| last menu.item-* has width 100px
Applying multiple checks for only first element from given expression
Allows to apply multiple specs to only first element
Syntax: first %{objectPattern}:
| first menu.item-* :
below header 10px
inside main_container 0px top left
Applying multiple checks for only last element from given expression
Allows to apply multiple specs to only last element
Syntax: last %{objectPattern}:
| last menu.item-* :
below header 10px
inside main_container 0px top left
Comments
We have moved all the discussions to Google Groups. From this moment, if you have problems with your test code or some issues with installation, please ask your questions in https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/galen-framework.